HTTP protocol
what is HTTP?
- HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol.
- The HTTP protocol can be used to transfer the data in the form of plain text, hypertext, audio, video, etc on the internet.
features of HTTP
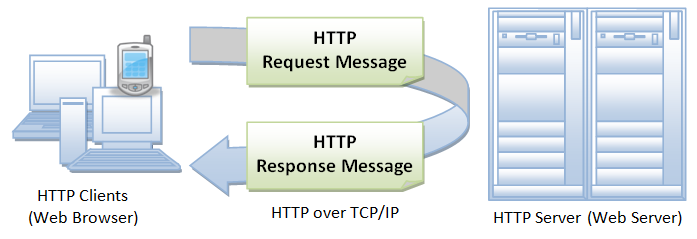
- HTTP is connectionless
- The HTTP client, i.e., a browser initiates an HTTP request and after a request is made, the client waits for the response.
- Server processes the request and returns the response.
- Once response is recieved then HTTP client disconnects the connection.
- HTTP is media independent
- The client has to specify the media type in the request
- Then server will understand the media request and processes it.
- HTTP is stateless
- The server and client are aware of each other only during a current request. Afterwards, both of them forget about each other.
HTTP Request
- It has two parts
HTTP request headers and HTTP request body
- The request looks something like below
http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/
POST /login/ HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; rv:18.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/18.0
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
DNT: 1
Referer: http://127.0.0.1:8000/login/
Cookie: passx=87e8af376bc9d9bfec2c7c0193e6af70; PHPSESSID=l9hk7mfh0ppqecg8gialak6gt5
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Type: multipart/form-data
HTTP request body
- HTTP Message Body is the data bytes transmitted in an HTTP transaction message immediately following the headers if there are any.
HTTP response:
- It also has two parts
HTTP response headers and HTTP response body
200 OK
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Connection: Keep-Alive
Content-Encoding: gzip
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Date: Mon, 18 Jul 2016 16:06:00 GMT
Etag: "c561c68d0ba92bbeb8b0f612a9199f722e3a621a"
Keep-Alive: timeout=5, max=997
Last-Modified: Mon, 18 Jul 2016 02:36:04 GMT
HTTP response body
- The last part of a response is the body. Not all responses have one: responses with a status code that sufficiently answers the request without the need for corresponding payload (like 201 Created or 204 No Content) usually don't.
HTTP status codes
- Informational responses (100 – 199)
- Successful responses (200 – 299)
- Redirection messages (300 – 399)
- Client error responses (400 – 499)
- Server error responses (500 – 599)
| Status code | Meaning |
| 1xx Informational | |
| 100 | Continue |
| 101 | Switching protocols |
| 102 | Processing |
| 103 | Early Hints |
| 2xx Succesful | |
| 200 | OK |
| 201 | Created |
| 202 | Accepted |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information |
| 204 | No Content |
| 205 | Reset Content |
| 206 | Partial Content |
| 207 | Multi-Status |
| 208 | Already Reported |
| 226 | IM Used |
| 3xx Redirection | |
| 300 | Multiple Choices |
| 301 | Moved Permanently |
| 302 | Found (Previously "Moved Temporarily") |
| 303 | See Other |
| 304 | Not Modified |
| 305 | Use Proxy |
| 306 | Switch Proxy |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect |
| 4xx Client Error | |
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 402 | Payment Required |
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 404 | Not Found |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed |
| 406 | Not Acceptable |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required |
| 408 | Request Timeout |
| 409 | Conflict |
| 410 | Gone |
| 411 | Length Required |
| 412 | Precondition Failed |
| 413 | Payload Too Large |
| 414 | URI Too Long |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type |
| 416 | Range Not Satisfiable |
| 417 | Expectation Failed |
| 418 | I'm a Teapot |
| 421 | Misdirected Request |
| 422 | Unprocessable Entity |
| 423 | Locked |
| 424 | Failed Dependency |
| 425 | Too Early |
| 426 | Upgrade Required |
| 428 | Precondition Required |
| 429 | Too Many Requests |
| 431 | Request Header Fields Too Large |
| 451 | Unavailable For Legal Reasons |
| 5xx Server Error | |
| 500 | Internal Server Error |
| 501 | Not Implemented |
| 502 | Bad Gateway |
| 503 | Service Unavailable |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout |
| 505 | HTTP Version Not Supported |
| 506 | Variant Also Negotiates |
| 507 | Insufficient Storage |
| 508 | Loop Detected |
| 510 | Not Extended |
| 511 | Network Authentication Required |
References:
